Different AML regulators around the globe
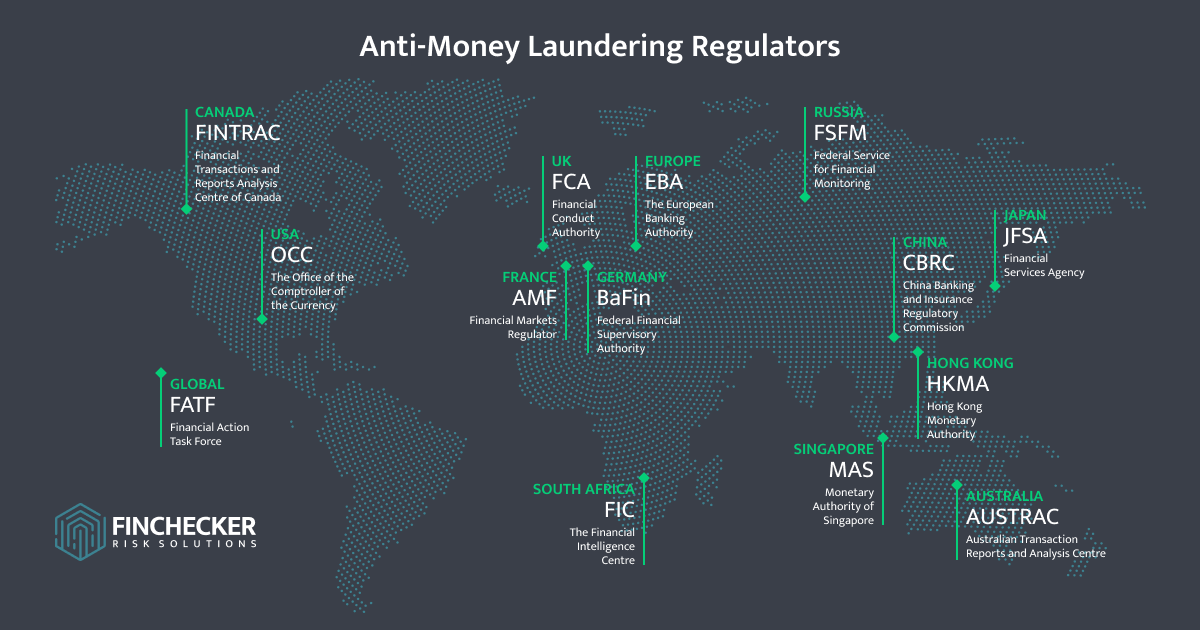
To combat financial crime and terrorism financing, financial institutions are held accountable to specific compliance obligations. These obligations are controlled by local and international authorities with varying perspectives but a common objective.
How is AML regulated globally?
FATF - The Financial Action Task Force an intergovernmental organization that establishes global standards to assist countries in creating and updating their legal frameworks to combat money laundering and financing of terrorism. In that respect FATF regularly releases guidance on AML and CTF regulations. The FATF currently has 37 member jurisdictions and 2 regional organizations, which represent the majority of the world's major financial centers.
European Union
EU 6AMLD
The European Union issues directive that promote the integrity and expansion of the financial system by preventing money laundering and the financing of terrorism on a global scale, which went into effect on December 2, 2018, and which member states were required to implement into domestic law by December 3, 2020. Laws within the European Union contain common elements as a result of the transposition of directives into national law, which is again similar to the influence exercised by FATF globally.
United Kingdom
FCA - The Financial Conduct Authority
The Financial Conduct Authority is an independent, non-governmental body regulatory organization in the United Kingdom. The objectives of FCA regulation are to defend consumers, improve market integrity, and foster competition. It has the power to oversee, authorize, and regulate in order to accomplish this goal.
The United states
The Bank Secrecy Act
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is the United State’s main anti-money laundering regulation and is administered by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). Although the BSA's primary focus is on money laundering, it has since broadened its purview to cover other financial crimes, such as countering terrorist financing (CTF) initiatives.
Singapore
Singapore will assume the FATF Presidency on July 1, 2022, for a set period of two years. The legal framework is also being updated by amending the recently passed Financial Services and Markets Bill as well as the Payment Services Act 2019. The Monetary Authority of Singapore has also released a new AML/CFT notice for financial institutions regarding the conduct of their operations and business activities in precious stones, precious metals, and precious products, in addition to publishing its Enforcement Report for the period of July 2020 to December 2021.
Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA)
The HKMA is responsible for ensuring the stability of Hong Kong's banking system and implementing monetary policies. It supervises financial institutions, manages reserves and assets, and seeks to strengthen Hong Kong's financial standing globally. Financial institutions must follow AML guidelines outlined by the HKMA in its Notices on Preventing Money Laundering and Tackling Financing of Terrorism. Key points in these guidelines include:
- Due Diligence: Financial institutions have to carry out strict due diligence on clients when there is suspicion of money laundering or terrorism financing. This helps maintain a secure financial system and guards against illegal activities.
- Know Your Customer: The identities of customers must be confirmed by independent checks. The checks must be recorded by Financial institutions.
- Financial institutions in Singapore are required to regularly review customer accounts, keep an eye out for suspicious activity, and report incidents to MAS.